Transformer 实现
我们采用 top-down 的形式构建 transformer 的代码
架构
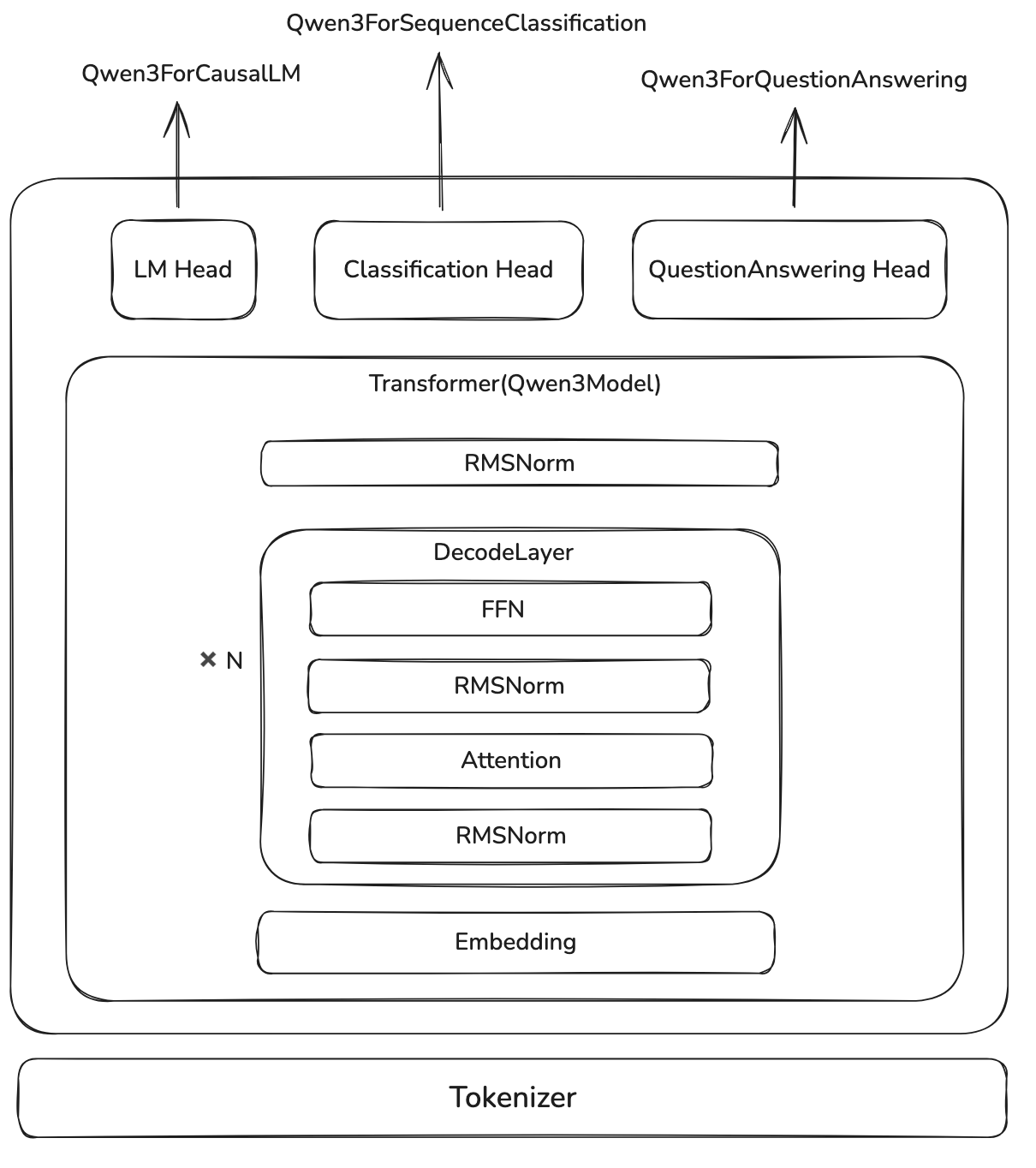
我们以 Qwen3 的代码为例子讲解 Assignment1 的代码实现
我们通过在 transformer 架构上加上一个 linear layer 就可以完成不同的下游任务,比如:
Qwen3ForQuestionAnsweringQwen3ForCausalLMQwen3ForSequenceClassification
因此,大语言模型是 transformer 的一个附加产物
CausalLM
编写大语言模型的第一步为定义 Qwen3ForCausalLM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| class CausalLM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
self.model = Transformer(config)
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.vocab_size, bias=False)
def forward(self, ...):
outputs = self.model(***)
logits = self.lm_head(outputs)
return logits
|
这里 lm_head 的作用就是构建 embedding space 到 vocabulary 的映射,即 $\mathbb{R}^d\to\mathbb{R}^{|V|}$
transformer 部分包括四个部分:
- Embedding Layer:将 token 映射到 embedding space
- layers:Transformer 的主体部分,由 $n$ 个
DecodeLayer 组成 - Norm:在输出之前,进行一次 Normalization
- Position Embedding:由于输入的 sequence 长度是固定的,因此我们提前计算好每一层的 position embedding
Transformer 部分的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, config.pad_token_id)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[DecodeLayer(config, layer_idx) for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]
)
self.norm = RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.rotary_emb = RotaryEmbedding(config)
def forward(self, input_ids,...):
input_embeds = self.embedding(input_ids)
hidden_states = input_embeds
position_embeddings = self.rotary_emb(hidden_states, position_ids)
for decode_layer in self.layers:
layer_outputs = decode_layer(hidden_states, position_ids, position_embeddings)
hidden_states = layer_outputs[0]
hidden_states = self.norm(hidden_states)
return logits
|
DecodeLayer
DecodeLayer 就是 transformer 的核心部分,里面包含四个模块:
- Pre-Normalization:一般是 RMSNorm 或者 LayerNorm
- Attention:self-attention
- Post-Normalization:与 Pre-Normalization 一致
- MLP:FFN,SwiGLU 或者 MoE
DecodeLayer 还会使用 residual connection 来防止梯度消失
DecodeLayer 部分的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class DecodeLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, layer_idx):
self.attn = Attention(config, layer_idx)
self.mlp = MLP(config)
self.pre_norm = RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.post_norm = RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
def forward(self, hidden_states, position_ids, position_embeddings):
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.pre_norm(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.attn(hidden_states, position_ids, position_embeddings)
# residual
hidden_states = hidden_states + residual
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.post_norm(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
# residual
hidden_states = hidden_states + residual
return hidden_states
|
我们接下来按照
- Normalization
- MLP
- Attention
- Position embedding
的顺序来介绍
RMSNorm
RMSNorm 的作用和 LayerNorm 是一样的,但是实现上更简单
$$
\mathrm{LayerNorm}(x) = \frac{x-\mathbb{E}[x]}{\sqrt{\mathrm{var}[x]+\epsilon}}\odot \beta + \gamma
$$其中 $\beta,\gamma\in\mathbb{R}^d$ 是可学习的参数
$$
\mathrm{RMSNorm}(x) = \frac{x}{\sqrt{\|x\|_2^2+\epsilon}}\odot \gamma
$$其中 $\gamma\in\mathbb{R}^d$ 是可学习的参数
RMSNorm 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class RMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d, eps):
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(d))
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, x):
input_dtype = x.dtype
x = x.to(torch.float32)
variance = x.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
x = x * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.eps)
return self.weight * x.to(input_dtype)
|
MLP
现在大语言模型的 MLP 使用的激活函数一般都是 SwiGLU, 其定义为
$$
\mathrm{SwiGLU}(x) = x\odot \sigma(x)
$$其中 $\sigma(\cdot)$ 是 sigmoid 函数
MLP 的定义为
$$
y = W_2(W_3x\odot \mathrm{SwiGLU}(W_1x))
$$其中 $W_3,W_1\in\mathbb{R}^{d_{ff}\times d}$, $W_2\in\mathbb{R}^{d\times d_{ff}}$
一般地,由于 FFN 只有两个权重矩阵,且 $d_{ff}=4d$, 在 SwiGLU 中,为了保证参数量一致,其隐藏层大小设置为 $d_{ff}'=\frac23d_{ff}=\frac83 d$.
MLP 的代码如下所示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| def SwiGLU(x):
return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d, d_ff):
self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(d, d_ff, bias=False)
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(d, d_ff, bias=False)
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(d_ff, d, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
return self.down_proj(SwiGLU(self.gate_proj(x)) * self.up_proj(x))
|
Attention
我们先不考虑 position embedding,直接看 attention,attention 定义为
$$
\mathrm{Attention}(X) = \mathrm{softmax}\left(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d}}\right)V\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times d}
$$其中 $X\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times d}$,
$$
Q = W_QX\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times d},\quad
K =W_KX\in\mathbb{R}^{n\times d},\quad
V = W_VX\in\mathbb{R}^{n\times d}
$$在自回归模型里,我们还会加上 mask, 让每个 token 只能看见前面的 token 的信息
$$
\mathrm{Attention}(X) = \mathrm{softmax}\left(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d}}\odot M\right)V
$$其中
$$
M = [M_{ij}] = \begin{cases}
1, &\text{ if } i < j\\
0, &\text{ otherwise}
\end{cases}
$$self-attention 的代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| def scaled_dot_product_attention(Q, K, V, mask) -> torch.Tensor:
d_k = Q.shape[-1] # d_k
scaled_factor = 1 / d_k**0.5
scores = torch.einsum("... s_q d_k, ... s_k d_k -> ... s_q s_k", Q, K)
scores *= scaled_factor
if mask is not None:
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, float("-inf"))
scores = scores.softmax(dim=-1)
return torch.einsum("... s_q s_k, ... s_k d_v -> ... s_q d_v", scores, V)
|
Multi-Head Attention
Multi-Head Attention 定义如下
$$
\mathrm{MultiHeadAttention}(X) = [\mathrm{Attention}_1(X),\dots,\mathrm{Attention}_h(X)]W_o\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times d}
$$其中 $W_o\in\mathbb{R}^{d\times d}$, 且每一个 Attention heads 的维度会从 $d\to d/h$.
Multi-Head Attention 的主要作用为:
- 让不同的 head 关注不同的信息
- 并行计算,提高计算效率
MHA 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model: int, num_heads: int) -> None:
self.q_proj = Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.k_proj = Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.v_proj = Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.output_proj = Linear(d_model, d_model,)
def forward(self, x, position_embeddings, mask):
Q = rearrange(self.q_proj(x), "... seq_len (num_heads head_dim) -> ... num_heads seq_len head_dim",
num_heads=self.num_heads, head_dim=self.head_dim)
K = rearrange( self.k_proj(x), "... seq_len (num_heads head_dim) -> ... num_heads seq_len head_dim",
num_heads=self.num_heads, head_dim=self.head_dim)
if mask is None:
mask = torch.ones(Q.shape[-2], K.shape[-2])
mask = torch.tril(mask)
if position_embeddings is not None:
sin, cos = position_embeddings
Q = apply_rotary_pos_emb(Q, sin, cos)
K = apply_rotary_pos_emb(K, sin, cos)
V = rearrange(self.v_proj(x), "... seq_len (num_heads head_dim) -> ... num_heads seq_len head_dim",
num_heads=self.num_heads, head_dim=self.head_dim)
output = scaled_dot_product_attention(Q, K, V, mask=mask)
output = rearrange(output, "... num_heads seq_len head_dim -> ... seq_len (num_heads head_dim)")
return self.output_proj(output)
|
Position Encoding
Attention 对于输入的顺序是不敏感的,也就是
$$
\mathrm{Attention}(Q, \Pi K, \Pi V) = \mathrm{Attention}(Q, K, V)
$$这里 $\Pi\in \{0,1\}^{d\times d}$ 是一个置换矩阵 (permutation matrix)
Transformer 的解决方法是在 query 和 key 上加上位置信息:
$$
Q' = Q + PE(Q),\ K'=K + PE(K)
$$这样
$$
\mathrm{Attention}(Q, K, V) = \mathrm{softmax}\left(\frac{(Q + PE(Q))(K + PE(K))^T}{\sqrt{d}}\right)V\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times d}
$$就包含了位置信息
绝对位置编码
Transformer 的使用的位置编码如下所示
$$
PE(pos, 2i) = \sin\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{2i/d}}\right)
$$$$
PE(pos, 2i+1) = \cos\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{2i/d}}\right)
$$RoPE
苏剑林老师提出了 Position Encoding,现在已经被广泛使用
$$
q' = R_{\theta,m}^dq, k' = R_{\theta,n}^d k
$$这样 $\langle q, k\rangle$ 就仅包含两者的相对位置信息
$$
\langle q_m, k_n\rangle = x^TW_qR_{\theta, n-m}^d W_kx_n
$$RoPE 的矩阵定义如下
$$
R_{\theta,m}^d = \mathrm{diag}(M_1,\dots,M_{d/2})
$$其中
$$
M_i = \begin{bmatrix}
\cos m\theta_i & -\sin m\theta_i\\
\sin m\theta_i & \cos m\theta_i
\end{bmatrix}
$$这里
$$
\theta_i = \frac{1}{10000^{2(i-1)/d}}, i\in\{1,2,\dots,d/2\}
$$简化后得到
$$
R_{\theta,m}^dq = \begin{bmatrix}
\cos m\theta_0\\
\cos m\theta_0\\
\vdots\\
\cos m\theta_{d/2}\\
\cos m\theta_{d/2}\\
\end{bmatrix}\odot \begin{bmatrix}
x1\\
x2\\
\vdots\\
x_{d-1}\\
x_d\\
\end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix}
\sin m\theta_0\\
\sin m\theta_0\\
\vdots\\
\sin m\theta_{d/2}\\
\sin m\theta_{d/2}\\
\end{bmatrix}\odot
\begin{bmatrix}
-\ x_2\\
x_1\\
\vdots\\
-x_d\\
x_{d-1}\\
\end{bmatrix}
$$RoPE 代码 Naive 实现
RotaryEmbedding 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class RotaryEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
self.inv_freq = 1.0 / (theta ** (torch.arange(0, dim, 2)[: (dim // 2)].float() / dim))
def forward(self, x, position_ids):
freqs = einsum(torch.arange(self.max_seq_len),
self.inv_freq, "seq_len, d_k_half -> seq_len d_k_half")[token_positions]
sin = torch.sin(freqs)
cos = torch.cos(freqs)
return sin, cos
|
计算部分代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| def apply_rotary_pos_emb(x: torch.Tensor, sin: torch.Tensor, cos: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x_even = x[..., ::2] # (seq_len, d_k_half)
x_odd = x[..., 1::2] # (seq_len, d_k_half)
odds = cos * x_even - sin * x_odd # (...,seq_len, d_k_half)
evens = sin * x_even + cos * x_odd # (...,seq_len, d_k_half)
stacked = torch.stack((odds, evens), -2) # (...,seq_len, 2, d_k_half)
stacked_trans = rearrange(
stacked, "... seq_len double d_k_half -> ... seq_len d_k_half double"
) # (...,seq_len, d_k_half, 2)
out = rearrange(
stacked_trans, "... seq_len d_k_half double -> ... seq_len (d_k_half double)"
) # (..., seq_len, d_k)
return out
|
RoPE 标准实现
RotaryEmbedding 代码 (LLaMA)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class LlamaRotaryEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: LlamaConfig, device=None):
inv_freq = inv_freq = 1.0 / (base ** (torch.arange(0, dim, 2, dtype=torch.int64) / dim)) # d_k_half
def forward(self, x, position_ids):
# (bsz, d_k_half, 1)
inv_freq_expanded = self.inv_freq[None, :, None].expand(position_ids.shape[0], -1, 1)
# (bsz, 1, seq_len)
position_ids_expanded = position_ids[:, None, :]
# (bsz, seq_len, d_k_half)
freqs = (inv_freq_expanded @ position_ids_expanded).transpose(1, 2)
emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1) # (..., seq_len, d_k)
cos = emb.cos() # (..., seq_len, d_k)
sin = emb.sin() # (..., seq_len, d_k)
return cos, sin
|
计算部分代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| def rotate_half(x):
x1 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2]
x2 = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :]
return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)
def apply_rotary_pos_emb(q, k, cos, sin, position_ids=None, unsqueeze_dim=1):
cos = cos.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
sin = sin.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin)
k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
return q_embed, k_embed
|
References
- Qwen3 transformer source code
- position encoding blog
