meta 等提出了 ALiBi, 一个通过 linear biases 来实现位置编码的方法来提高 LLM 在推理阶段的外推能力。
Introduction
当下,有若干种位置编码的方式:
作者通过实验对比了不同的位置编码方法,发现这些方法在推理阶段的外推能力都比较差。
为了解决这个问题,作者提出了 ALiBi (attention with linear biases), 一个几乎不增加计算和内存开销的位置编码方法,来提高 LLM 在推理阶段的外推能力。
Method
作者将外推能力定义为
a model’s ability to continue performing well as the number of input tokens during validation increases beyond the number of tokens on which the the model was trained.
计 $L$ 为训练阶段的上下文长度, $L_{valid}$ 为推理阶段的上下文长度。
作者首先对比了不同的位置编码方法的外推能力,结果如下图所示
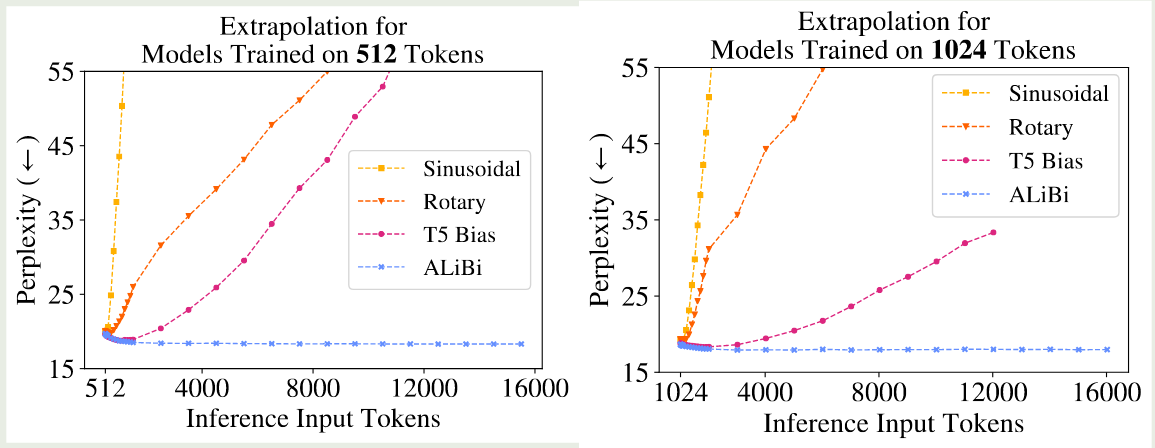
结果显示,不同位置编码在推理阶段扩展模型的上下文能力均有限。
| Context Length | $L$ | $L_{valid}$ |
|---|---|---|
| Sinusoidal | 512 | 50 |
| 1024 | 50 | |
| RoPE | 512 | 200 |
| 1024 | 100 | |
| T5 bias | 512 | 600 |
| 1024 | 800 | |
| ALiBi | 512 | - |
| 1024 | - |
为了解决这个问题,作者提出了 AliBi, 其表达式为
$$ \mathrm{softmax}(q_iK^T+m\cdot [-(i-1),\dots,-2,-1,0]) $$其中 $m$ 是一个和 heads 相关的超参数。如果我们有 8 个 heads, 则对应的 scaling 值分别为 $[1/2^1,1/2^2,\dots,1/2^8]$, 如果我们有 16 个 heads, 则我们对 8 个 heads 的结果进行插值,得到 $[1/2^{0.5},1/2^1,\dots,1/2^8]$. ALiBi 的示意图如下所示
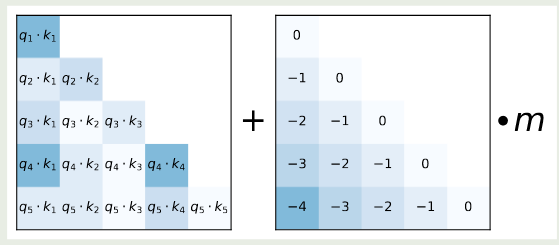
ALiBi 通过 bias 惩罚了较远的 query-key pairs, 并且不同的 heads 的惩罚项也不同,从而每个 head 对距离的信息敏感度也不尽相同。
Experiments
ALiBi 在 WikiText-103 上的实验结果如下图所示
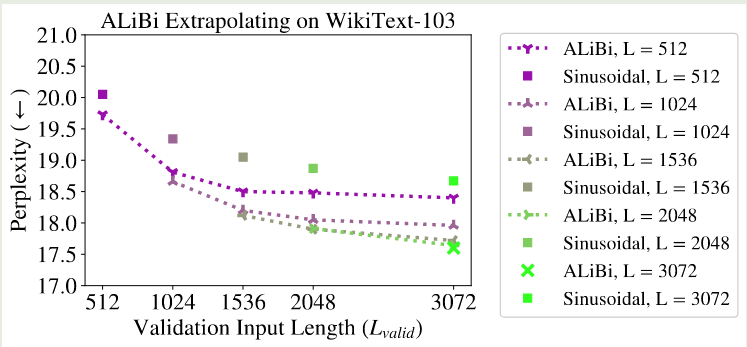
Conclusion
作者分析了已有的 position embedding 方法,发现已有的方法在推理阶段均不能有效扩展模型的上下文长度。因此,作者提出了 AliBi, 一个通过 linear bias 来增加位置信息的方法,作者通过实验验证了 ALiBi 的有效性。