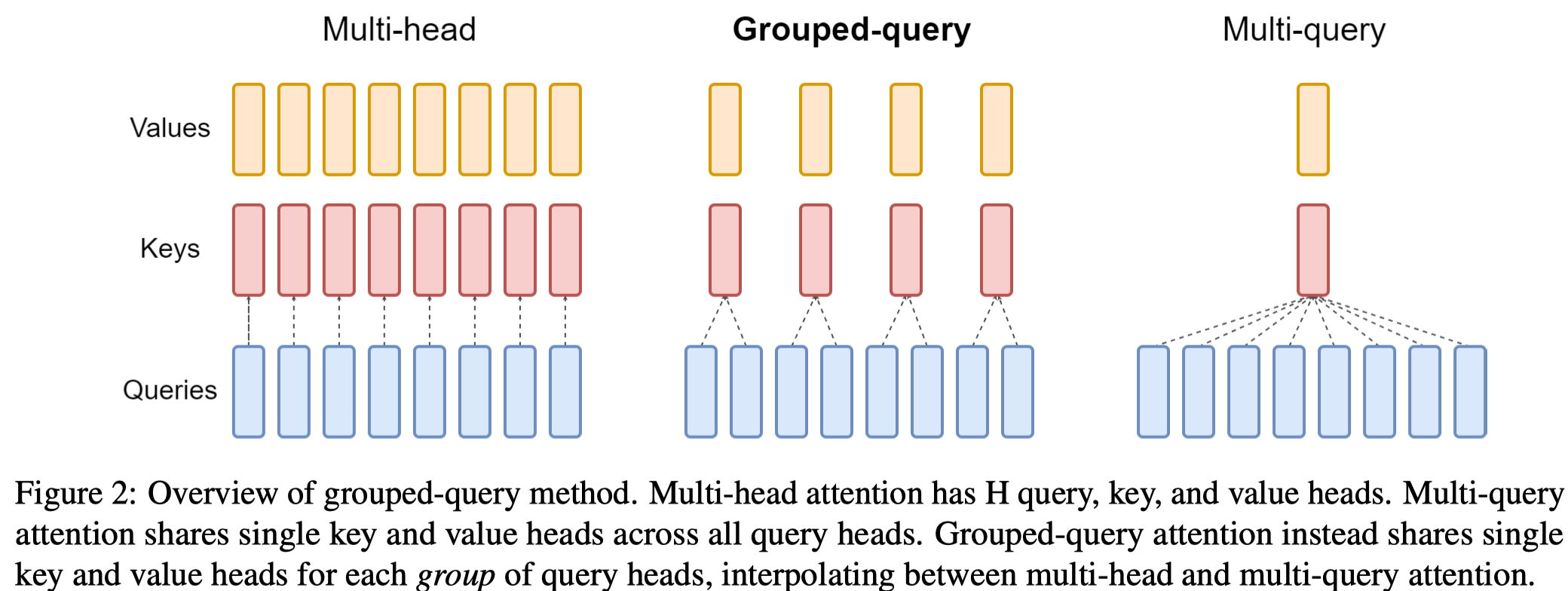
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| def repeat_kv(hidden_states: torch.Tensor, n_rep: int) -> torch.Tensor:
batch, num_key_value_heads, slen, head_dim = hidden_states.shape
if n_rep == 1:
return hidden_states
hidden_states = hidden_states[:, :, None, :, :].expand(batch, num_key_value_heads, n_rep, slen, head_dim)
return hidden_states.reshape(batch, num_key_value_heads * n_rep, slen, head_dim)
def eager_attention_forward(
module: nn.Module,
query: torch.Tensor,
key: torch.Tensor,
value: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor],
scaling: float,
dropout: float = 0.0,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
):
key_states = repeat_kv(key, module.num_key_value_groups)
value_states = repeat_kv(value, module.num_key_value_groups)
attn_weights = torch.matmul(query, key_states.transpose(2, 3)) * scaling
if attention_mask is not None:
causal_mask = attention_mask[:, :, :, : key_states.shape[-2]]
attn_weights = attn_weights + causal_mask
attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32).to(query.dtype)
attn_weights = nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=dropout, training=module.training)
attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value_states)
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
return attn_output, attn_weights
class Qwen3Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3Config, layer_idx: int):
super().__init__()
self.head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads)
self.scaling = self.head_dim**-0.5
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.o_proj = nn.Linear(
config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim, config.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias
)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
position_embeddings: tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor],
past_key_value: Optional[Cache] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
input_shape = hidden_states.shape[:-1]
hidden_shape = (*input_shape, -1, self.head_dim)
query_states = self.q_norm(self.q_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2)
key_states = self.k_norm(self.k_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2)
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape).transpose(1, 2)
cos, sin = position_embeddings
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
attn_output, attn_weights = eager_attention_forward(
self,
query_states,
key_states,
value_states,
attention_mask,
dropout=0.0,
scaling=self.scaling,
sliding_window=self.sliding_window, # diff with Llama
**kwargs,
)
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(*input_shape, -1).contiguous()
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output)
return attn_output, attn_weights
|