Introduction
【参考文献 1】中系统性对比了 AliBi, RoPE , T5 提出的 T5 bias 以及 Transformer 提出的绝对位置编码 (APE).
作者发现,常用的方法在 length generalization 上表现并不是最好的,而 NoPE 不需要额外的计算开销反而效果最好。
【参考文献 2】 进一步探究了 NoPE 长度外推的泛化性。作者有三点发现:
- NoPE 相比于 RoPE, 其长度外推泛化能力更强
- 对于 NoPE 来说,模型会在还没有到达预训练上下文长度之前,表现就出现下降的情况
- 通过调整 softmax 的温度超参数,我们可以提高 NoPE 的长度外推泛化性能力。
Method
【参考文献 1】对比了不同 position encoding 的相似度,结果如下图所示
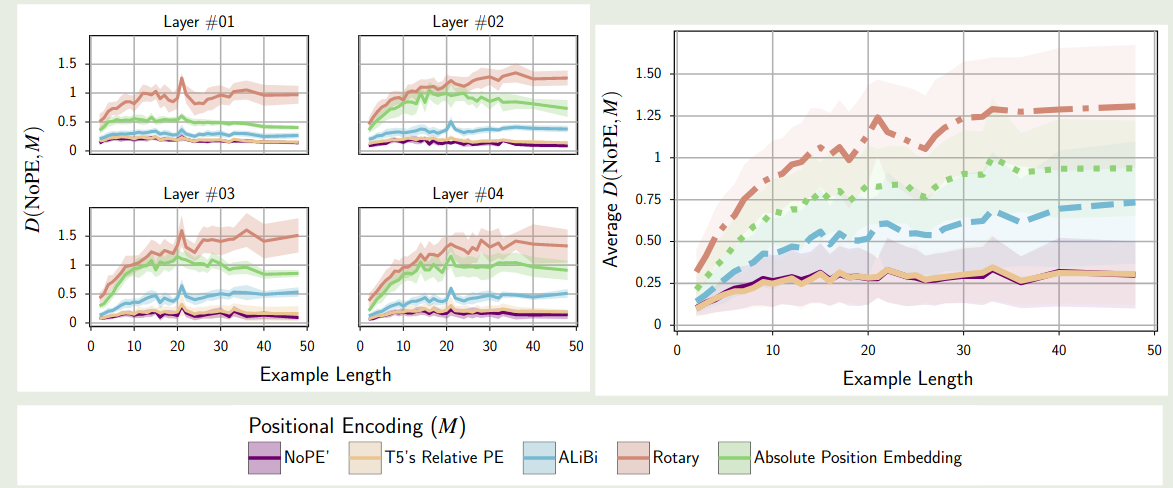
实验结果表明,NoPE 与 T5 提出的 T5 bias 最相似。
作者在理论上推导出了 NoPE 的两个性质:
Theorem 1 (Absolute Encoding) Let $x$ be an input sequence of length $T + 1$ to the model. Then, the first layer of $f_θ$ can recover absolute positions $[1, . . . , T + 1]$ in the hidden state $H^{(1)}$. That is, there exist $W_Q, W_K , W_V , W_O, W_1$, and $W_2$ such that the self-attention and feedforward operations in the first layer compute absolute positions and write it to the next hidden state.
Theorem 2 (Relative Encoding) Suppose that the hidden state $H^{(1)}$ contains absolute positional information, as stated in Theorem 1, and assume that it is not overwritten by any subsequent layers. Then, the self-attention in all subsequent layers can implement a relative positional encoding: there exists a parameterization of fθ such that, for $\ell ≥ 2$, the attention dot product between query $q_n$ and key $k_m$ at positions n and m can be expressed as:
$$ \langle q_n, k_m\rangle = f_{cnt}(q, k) + f_{rel}(n − m) $$where $f_{cnt}$ is a function of their content, and $f_{rel}$ is a function of their relative distance.
【参考文献 2】探究了 softmax 中 normalization factor 对模型表现的影响,作者定义 attention 为
$$ \mathrm{Attn}(q,k,v) = \mathrm{softmax}\left(\lambda q^Tk\right)v $$实验结果如下图所示
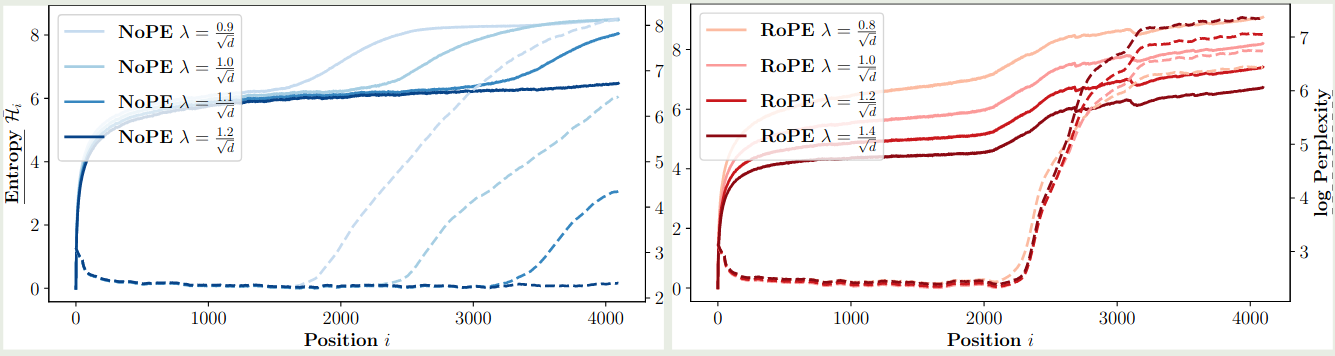
结果说明,通过调整 $\lambda$ 我们可以有效提高 NoPE 的上下文扩展泛化能力
Conclusion
NoPE 说明在 transformer 中我们可以不需要加入位置编码模块,这两篇论文均验证了 NoPE 的有效性。